Flex
Demonstrates the flex layout
variants.
git clone https://github.com/ratatui/ratatui.git --branch latestcd ratatuicargo run --example=flex --features=crossterm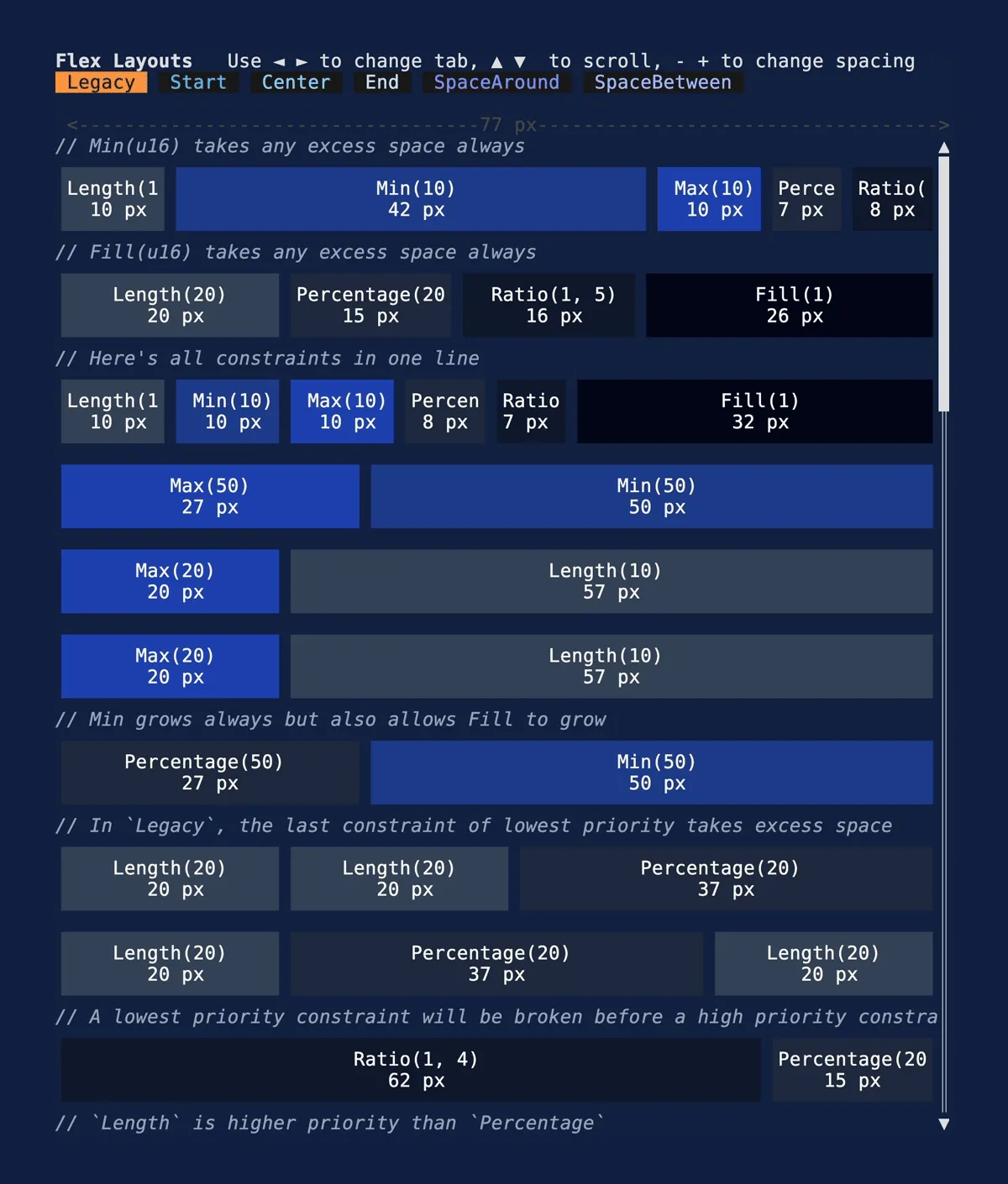
//! # [Ratatui] Flex example//!//! The latest version of this example is available in the [examples] folder in the repository.//!//! Please note that the examples are designed to be run against the `main` branch of the Github//! repository. This means that you may not be able to compile with the latest release version on//! crates.io, or the one that you have installed locally.//!//! See the [examples readme] for more information on finding examples that match the version of the//! library you are using.//!//! [Ratatui]: https://github.com/ratatui/ratatui//! [examples]: https://github.com/ratatui/ratatui/blob/main/examples//! [examples readme]: https://github.com/ratatui/ratatui/blob/main/examples/README.md
use std::num::NonZeroUsize;
use color_eyre::Result;use ratatui::{ buffer::Buffer, crossterm::event::{self, Event, KeyCode, KeyEventKind}, layout::{ Alignment, Constraint::{self, Fill, Length, Max, Min, Percentage, Ratio}, Flex, Layout, Rect, }, style::{palette::tailwind, Color, Modifier, Style, Stylize}, symbols::{self, line}, text::{Line, Text}, widgets::{ block::Title, Block, Paragraph, Scrollbar, ScrollbarOrientation, ScrollbarState, StatefulWidget, Tabs, Widget, }, DefaultTerminal,};use strum::{Display, EnumIter, FromRepr, IntoEnumIterator};
fn main() -> Result<()> { color_eyre::install()?; let terminal = ratatui::init(); let app_result = App::default().run(terminal); ratatui::restore(); app_result}
const EXAMPLE_DATA: &[(&str, &[Constraint])] = &[ ( "Min(u16) takes any excess space always", &[Length(10), Min(10), Max(10), Percentage(10), Ratio(1,10)], ), ( "Fill(u16) takes any excess space always", &[Length(20), Percentage(20), Ratio(1, 5), Fill(1)], ), ( "Here's all constraints in one line", &[Length(10), Min(10), Max(10), Percentage(10), Ratio(1,10), Fill(1)], ), ( "", &[Max(50), Min(50)], ), ( "", &[Max(20), Length(10)], ), ( "", &[Max(20), Length(10)], ), ( "Min grows always but also allows Fill to grow", &[Percentage(50), Fill(1), Fill(2), Min(50)], ), ( "In `Legacy`, the last constraint of lowest priority takes excess space", &[Length(20), Length(20), Percentage(20)], ), ("", &[Length(20), Percentage(20), Length(20)]), ("A lowest priority constraint will be broken before a high priority constraint", &[Ratio(1,4), Percentage(20)]), ("`Length` is higher priority than `Percentage`", &[Percentage(20), Length(10)]), ("`Min/Max` is higher priority than `Length`", &[Length(10), Max(20)]), ("", &[Length(100), Min(20)]), ("`Length` is higher priority than `Min/Max`", &[Max(20), Length(10)]), ("", &[Min(20), Length(90)]), ("Fill is the lowest priority and will fill any excess space", &[Fill(1), Ratio(1, 4)]), ("Fill can be used to scale proportionally with other Fill blocks", &[Fill(1), Percentage(20), Fill(2)]), ("", &[Ratio(1, 3), Percentage(20), Ratio(2, 3)]), ("Legacy will stretch the last lowest priority constraint\nStretch will only stretch equal weighted constraints", &[Length(20), Length(15)]), ("", &[Percentage(20), Length(15)]), ("`Fill(u16)` fills up excess space, but is lower priority to spacers.\ni.e. Fill will only have widths in Flex::Stretch and Flex::Legacy", &[Fill(1), Fill(1)]), ("", &[Length(20), Length(20)]), ( "When not using `Flex::Stretch` or `Flex::Legacy`,\n`Min(u16)` and `Max(u16)` collapse to their lowest values", &[Min(20), Max(20)], ), ( "", &[Max(20)], ), ("", &[Min(20), Max(20), Length(20), Length(20)]), ("", &[Fill(0), Fill(0)]), ( "`Fill(1)` can be to scale with respect to other `Fill(2)`", &[Fill(1), Fill(2)], ), ( "", &[Fill(1), Min(10), Max(10), Fill(2)], ), ( "`Fill(0)` collapses if there are other non-zero `Fill(_)`\nconstraints. e.g. `[Fill(0), Fill(0), Fill(1)]`:", &[ Fill(0), Fill(0), Fill(1), ], ),];
#[derive(Default, Clone, Copy)]struct App { selected_tab: SelectedTab, scroll_offset: u16, spacing: u16, state: AppState,}
#[derive(Debug, Default, Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq)]enum AppState { #[default] Running, Quit,}
#[derive(Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Eq)]struct Example { constraints: Vec<Constraint>, description: String, flex: Flex, spacing: u16,}
/// Tabs for the different layouts////// Note: the order of the variants will determine the order of the tabs this uses several derive/// macros from the `strum` crate to make it easier to iterate over the variants./// (`FromRepr`,`Display`,`EnumIter`).#[derive(Default, Debug, Copy, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, FromRepr, Display, EnumIter)]enum SelectedTab { #[default] Legacy, Start, Center, End, SpaceAround, SpaceBetween,}
impl App { fn run(mut self, mut terminal: DefaultTerminal) -> Result<()> { // increase the layout cache to account for the number of layout events. This ensures that // layout is not generally reprocessed on every frame (which would lead to possible janky // results when there are more than one possible solution to the requested layout). This // assumes the user changes spacing about a 100 times or so. let cache_size = EXAMPLE_DATA.len() * SelectedTab::iter().len() * 100; Layout::init_cache(NonZeroUsize::new(cache_size).unwrap());
while self.is_running() { terminal.draw(|frame| frame.render_widget(self, frame.area()))?; self.handle_events()?; } Ok(()) }
fn is_running(self) -> bool { self.state == AppState::Running }
fn handle_events(&mut self) -> Result<()> { match event::read()? { Event::Key(key) if key.kind == KeyEventKind::Press => match key.code { KeyCode::Char('q') | KeyCode::Esc => self.quit(), KeyCode::Char('l') | KeyCode::Right => self.next(), KeyCode::Char('h') | KeyCode::Left => self.previous(), KeyCode::Char('j') | KeyCode::Down => self.down(), KeyCode::Char('k') | KeyCode::Up => self.up(), KeyCode::Char('g') | KeyCode::Home => self.top(), KeyCode::Char('G') | KeyCode::End => self.bottom(), KeyCode::Char('+') => self.increment_spacing(), KeyCode::Char('-') => self.decrement_spacing(), _ => (), }, _ => {} } Ok(()) }
fn next(&mut self) { self.selected_tab = self.selected_tab.next(); }
fn previous(&mut self) { self.selected_tab = self.selected_tab.previous(); }
fn up(&mut self) { self.scroll_offset = self.scroll_offset.saturating_sub(1); }
fn down(&mut self) { self.scroll_offset = self .scroll_offset .saturating_add(1) .min(max_scroll_offset()); }
fn top(&mut self) { self.scroll_offset = 0; }
fn bottom(&mut self) { self.scroll_offset = max_scroll_offset(); }
fn increment_spacing(&mut self) { self.spacing = self.spacing.saturating_add(1); }
fn decrement_spacing(&mut self) { self.spacing = self.spacing.saturating_sub(1); }
fn quit(&mut self) { self.state = AppState::Quit; }}
// when scrolling, make sure we don't scroll past the last examplefn max_scroll_offset() -> u16 { example_height() - EXAMPLE_DATA .last() .map_or(0, |(desc, _)| get_description_height(desc) + 4)}
/// The height of all examples combined////// Each may or may not have a title so we need to account for that.fn example_height() -> u16 { EXAMPLE_DATA .iter() .map(|(desc, _)| get_description_height(desc) + 4) .sum()}
impl Widget for App { fn render(self, area: Rect, buf: &mut Buffer) { let layout = Layout::vertical([Length(3), Length(1), Fill(0)]); let [tabs, axis, demo] = layout.areas(area); self.tabs().render(tabs, buf); let scroll_needed = self.render_demo(demo, buf); let axis_width = if scroll_needed { axis.width.saturating_sub(1) } else { axis.width }; Self::axis(axis_width, self.spacing).render(axis, buf); }}
impl App { fn tabs(self) -> impl Widget { let tab_titles = SelectedTab::iter().map(SelectedTab::to_tab_title); let block = Block::new() .title(Title::from("Flex Layouts ".bold())) .title(" Use ◄ ► to change tab, ▲ ▼ to scroll, - + to change spacing "); Tabs::new(tab_titles) .block(block) .highlight_style(Modifier::REVERSED) .select(self.selected_tab as usize) .divider(" ") .padding("", "") }
/// a bar like `<----- 80 px (gap: 2 px)? ----->` fn axis(width: u16, spacing: u16) -> impl Widget { let width = width as usize; // only show gap when spacing is not zero let label = if spacing != 0 { format!("{width} px (gap: {spacing} px)") } else { format!("{width} px") }; let bar_width = width.saturating_sub(2); // we want to `<` and `>` at the ends let width_bar = format!("<{label:-^bar_width$}>"); Paragraph::new(width_bar.dark_gray()).centered() }
/// Render the demo content /// /// This function renders the demo content into a separate buffer and then splices the buffer /// into the main buffer. This is done to make it possible to handle scrolling easily. /// /// Returns bool indicating whether scroll was needed #[allow(clippy::cast_possible_truncation)] fn render_demo(self, area: Rect, buf: &mut Buffer) -> bool { // render demo content into a separate buffer so all examples fit we add an extra // area.height to make sure the last example is fully visible even when the scroll offset is // at the max let height = example_height(); let demo_area = Rect::new(0, 0, area.width, height); let mut demo_buf = Buffer::empty(demo_area);
let scrollbar_needed = self.scroll_offset != 0 || height > area.height; let content_area = if scrollbar_needed { Rect { width: demo_area.width - 1, ..demo_area } } else { demo_area };
let mut spacing = self.spacing; self.selected_tab .render(content_area, &mut demo_buf, &mut spacing);
let visible_content = demo_buf .content .into_iter() .skip((area.width * self.scroll_offset) as usize) .take(area.area() as usize); for (i, cell) in visible_content.enumerate() { let x = i as u16 % area.width; let y = i as u16 / area.width; buf[(area.x + x, area.y + y)] = cell; }
if scrollbar_needed { let area = area.intersection(buf.area); let mut state = ScrollbarState::new(max_scroll_offset() as usize) .position(self.scroll_offset as usize); Scrollbar::new(ScrollbarOrientation::VerticalRight).render(area, buf, &mut state); } scrollbar_needed }}
impl SelectedTab { /// Get the previous tab, if there is no previous tab return the current tab. fn previous(self) -> Self { let current_index: usize = self as usize; let previous_index = current_index.saturating_sub(1); Self::from_repr(previous_index).unwrap_or(self) }
/// Get the next tab, if there is no next tab return the current tab. fn next(self) -> Self { let current_index = self as usize; let next_index = current_index.saturating_add(1); Self::from_repr(next_index).unwrap_or(self) }
/// Convert a `SelectedTab` into a `Line` to display it by the `Tabs` widget. fn to_tab_title(value: Self) -> Line<'static> { use tailwind::{INDIGO, ORANGE, SKY}; let text = value.to_string(); let color = match value { Self::Legacy => ORANGE.c400, Self::Start => SKY.c400, Self::Center => SKY.c300, Self::End => SKY.c200, Self::SpaceAround => INDIGO.c400, Self::SpaceBetween => INDIGO.c300, }; format!(" {text} ").fg(color).bg(Color::Black).into() }}
impl StatefulWidget for SelectedTab { type State = u16; fn render(self, area: Rect, buf: &mut Buffer, spacing: &mut Self::State) { let spacing = *spacing; match self { Self::Legacy => Self::render_examples(area, buf, Flex::Legacy, spacing), Self::Start => Self::render_examples(area, buf, Flex::Start, spacing), Self::Center => Self::render_examples(area, buf, Flex::Center, spacing), Self::End => Self::render_examples(area, buf, Flex::End, spacing), Self::SpaceAround => Self::render_examples(area, buf, Flex::SpaceAround, spacing), Self::SpaceBetween => Self::render_examples(area, buf, Flex::SpaceBetween, spacing), } }}
impl SelectedTab { fn render_examples(area: Rect, buf: &mut Buffer, flex: Flex, spacing: u16) { let heights = EXAMPLE_DATA .iter() .map(|(desc, _)| get_description_height(desc) + 4); let areas = Layout::vertical(heights).flex(Flex::Start).split(area); for (area, (description, constraints)) in areas.iter().zip(EXAMPLE_DATA.iter()) { Example::new(constraints, description, flex, spacing).render(*area, buf); } }}
impl Example { fn new(constraints: &[Constraint], description: &str, flex: Flex, spacing: u16) -> Self { Self { constraints: constraints.into(), description: description.into(), flex, spacing, } }}
impl Widget for Example { fn render(self, area: Rect, buf: &mut Buffer) { let title_height = get_description_height(&self.description); let layout = Layout::vertical([Length(title_height), Fill(0)]); let [title, illustrations] = layout.areas(area);
let (blocks, spacers) = Layout::horizontal(&self.constraints) .flex(self.flex) .spacing(self.spacing) .split_with_spacers(illustrations);
if !self.description.is_empty() { Paragraph::new( self.description .split('\n') .map(|s| format!("// {s}").italic().fg(tailwind::SLATE.c400)) .map(Line::from) .collect::<Vec<Line>>(), ) .render(title, buf); }
for (block, constraint) in blocks.iter().zip(&self.constraints) { Self::illustration(*constraint, block.width).render(*block, buf); }
for spacer in spacers.iter() { Self::render_spacer(*spacer, buf); } }}
impl Example { fn render_spacer(spacer: Rect, buf: &mut Buffer) { if spacer.width > 1 { let corners_only = symbols::border::Set { top_left: line::NORMAL.top_left, top_right: line::NORMAL.top_right, bottom_left: line::NORMAL.bottom_left, bottom_right: line::NORMAL.bottom_right, vertical_left: " ", vertical_right: " ", horizontal_top: " ", horizontal_bottom: " ", }; Block::bordered() .border_set(corners_only) .border_style(Style::reset().dark_gray()) .render(spacer, buf); } else { Paragraph::new(Text::from(vec![ Line::from(""), Line::from("│"), Line::from("│"), Line::from(""), ])) .style(Style::reset().dark_gray()) .render(spacer, buf); } let width = spacer.width; let label = if width > 4 { format!("{width} px") } else if width > 2 { format!("{width}") } else { String::new() }; let text = Text::from(vec![ Line::raw(""), Line::raw(""), Line::styled(label, Style::reset().dark_gray()), ]); Paragraph::new(text) .style(Style::reset().dark_gray()) .alignment(Alignment::Center) .render(spacer, buf); }
fn illustration(constraint: Constraint, width: u16) -> impl Widget { let main_color = color_for_constraint(constraint); let fg_color = Color::White; let title = format!("{constraint}"); let content = format!("{width} px"); let text = format!("{title}\n{content}"); let block = Block::bordered() .border_set(symbols::border::QUADRANT_OUTSIDE) .border_style(Style::reset().fg(main_color).reversed()) .style(Style::default().fg(fg_color).bg(main_color)); Paragraph::new(text).centered().block(block) }}
const fn color_for_constraint(constraint: Constraint) -> Color { use tailwind::{BLUE, SLATE}; match constraint { Constraint::Min(_) => BLUE.c900, Constraint::Max(_) => BLUE.c800, Constraint::Length(_) => SLATE.c700, Constraint::Percentage(_) => SLATE.c800, Constraint::Ratio(_, _) => SLATE.c900, Constraint::Fill(_) => SLATE.c950, }}
#[allow(clippy::cast_possible_truncation)]fn get_description_height(s: &str) -> u16 { if s.is_empty() { 0 } else { s.split('\n').count() as u16 }}
